Introduction –
Paytm, short for “Pay Through Mobile,” is a renowned Indian fintech company that has disrupted the traditional financial and payment landscape in India. Established in 2010 by entrepreneur Vijay Shekhar Sharma, Paytm’s business model has evolved from its inception as a mobile recharge and bill payment platform to become a comprehensive digital payment and financial services ecosystem.
This introduction provides a glimpse into the key aspects of Paytm’s business model and its transformative impact on the way people in India conduct financial transactions, shop online, and access a range of financial services. Paytm’s journey reflects the broader trends in the Indian fintech industry and the changing dynamics of digital finance in the country.
What is the Business Model of PAYTM Company?
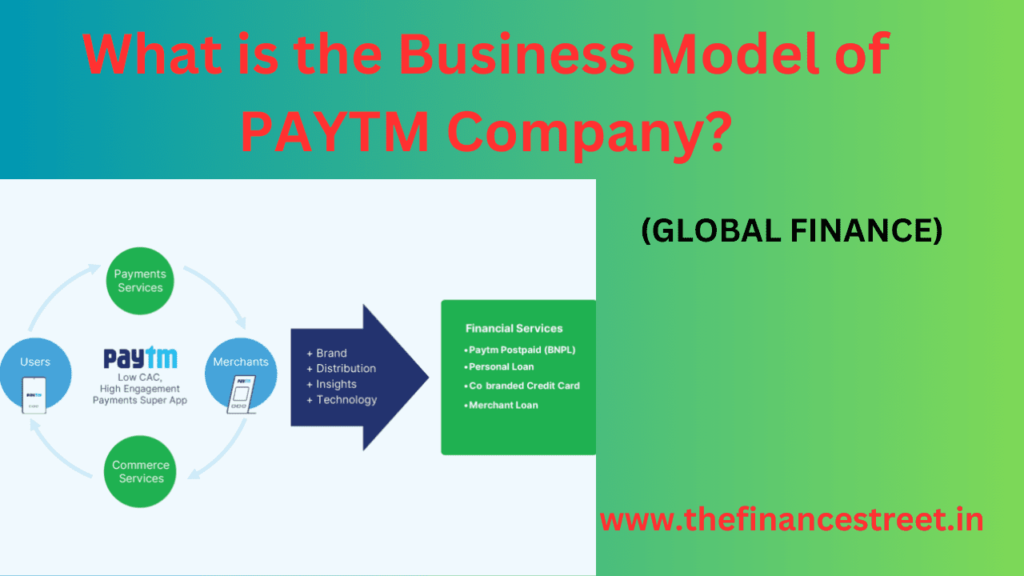
Paytm, an Indian fintech company founded in 2010, operates on a multifaceted business model that encompasses various financial services and e-commerce activities. At its core, Paytm began as a mobile wallet and digital payments platform, but it has since expanded into a diverse range of services. Here’s an overview of the key components of Paytm’s business model:
- Digital Payments: Paytm’s initial focus was on digital payments. Users can link their bank accounts and credit/debit cards to the Paytm app and use it for a wide range of transactions, including mobile recharges, utility bill payments, online shopping, and in-store payments through QR codes. Paytm enables peer-to-peer (P2P) payments and facilitates money transfers.
- Mobile Wallet: Paytm offers a mobile wallet, which allows users to store money digitally. This wallet can be funded using various payment methods, including credit/debit cards and bank transfers. Users can then use the wallet balance for making payments or transferring money to others.
- E-commerce Marketplace: Paytm has evolved into a significant e-commerce platform, where users can buy a wide range of products, including electronics, fashion items, groceries, and more. Paytm Mall, the e-commerce arm of Paytm, competes with other major Indian e-commerce players.
- Financial Services: Paytm offers a suite of financial services, including insurance, mutual funds, gold purchases, and loans. Users can invest in mutual funds, purchase insurance policies, buy digital gold, and apply for personal loans through the platform.
- Travel Booking: Paytm provides travel booking services for flights, buses, trains, and hotels. Users can book tickets and accommodations directly through the app.
- Utility Bill Payments: Users can pay their electricity, water, gas, and other utility bills through Paytm, consolidating various payment needs into a single platform.
- Online-to-Offline (O2O) Services: Paytm has expanded into the O2O space by allowing users to make payments and book services at offline merchants, including restaurants, grocery stores, and more. This is facilitated through QR code payments and integration with offline businesses.
- Cashback and Loyalty Programs: Paytm has a robust cashback and loyalty program where users receive cashback rewards and discounts for making payments and purchases through the platform. These incentives encourage user engagement and loyalty.
- Business Solutions: Paytm provides a range of solutions for businesses, including payment processing services, point-of-sale (PoS) devices, and integration options for e-commerce and offline merchants.
- Paytm Payments Bank: Paytm also operates a Payments Bank, which offers savings accounts, fixed deposits, and debit cards. Customers can earn interest on their account balances.
Paytm’s diverse business model has enabled it to become one of the leading fintech companies in India, offering a comprehensive suite of financial and e-commerce services to both consumers and businesses. As the digital payments and financial services landscape evolves, Paytm continues to innovate and expand its offerings to meet the changing needs of its users.
What is the success Journey of of PAYTM company?
The journey of Paytm (short for “Pay Through Mobile”) is a remarkable success story in the Indian fintech and e-commerce industry. Founded in 2010 by Vijay Shekhar Sharma, Paytm has grown from a startup offering mobile recharge and utility bill payments to one of India’s leading digital payment platforms and e-commerce marketplaces. Here is an overview of Paytm’s success journey:
- Founding and Early Growth (2010-2014):
- Paytm was founded by Vijay Shekhar Sharma, an entrepreneur with a vision to simplify digital payments and make them accessible to a wide audience in India.
- The company initially focused on mobile recharge and bill payments, providing a convenient way for users to top up their mobile phones and settle utility bills.
- Paytm’s early success was driven by its user-friendly mobile app and a focus on providing cashback offers and discounts to attract and retain customers.
- Expansion into E-commerce (2014-2016):
- In 2014, Paytm entered the e-commerce space by launching Paytm Mall, an online marketplace offering a wide range of products, including electronics, fashion, and more.
- The company capitalized on the growing popularity of online shopping in India and positioned itself as a one-stop-shop for digital payments and e-commerce.
- Strategic partnerships with various brands and sellers further fueled Paytm’s growth in the e-commerce sector.
- Funding and Investment (2015-2017):
- Paytm attracted significant funding from investors, including Alibaba Group and Ant Financial (an affiliate of Alibaba), which collectively invested billions of dollars in the company.
- These investments provided the capital needed for expansion and innovation, allowing Paytm to enhance its product offerings and scale its operations.
- Diversification of Services (2017-Present):
- Paytm diversified its services to include financial products such as insurance, mutual funds, and digital gold purchases. Users could invest and insure through the platform.
- The company also ventured into the travel booking sector, offering flight, train, bus, and hotel bookings.
- Paytm continued to expand its offline-to-online (O2O) services, enabling users to make payments at brick-and-mortar stores and book services such as movie tickets and restaurant reservations.
- Paytm Payments Bank (2017):
- Paytm received approval from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to launch Paytm Payments Bank in 2017. The bank offers savings accounts, fixed deposits, and debit cards to customers.
- This move allowed Paytm to offer a more comprehensive suite of financial services while adhering to regulatory requirements.
- Uplifting Digital Payments (Demonetization):
- The Indian government’s demonetization move in 2016, which involved the withdrawal of high-denomination currency notes, gave a significant boost to digital payments in India.
- Paytm, as a leading digital payment platform, benefited from this trend, experiencing a surge in users and transactions.
- IPO Plans and Continued Growth:
- In 2021, Paytm announced plans for an initial public offering (IPO), a significant milestone for the company. The IPO was intended to raise funds for further expansion and innovation.
- Paytm continued to invest in technology, artificial intelligence, and user experience enhancements to maintain its competitive edge.
Paytm’s journey from a mobile recharge and bill payment platform to a multifaceted fintech and e-commerce powerhouse is a testament to its adaptability, innovative spirit, and ability to capture opportunities in India’s evolving digital landscape. The company has played a crucial role in advancing digital payments and financial inclusion in the country, and its success story continues to inspire the Indian startup ecosystem.
What are the Compatative advantages of PAYTM?
Paytm, as a prominent player in India’s fintech and digital payment ecosystem, has several competitive advantages that have contributed to its success and market leadership. These advantages include:
- Strong User Base: Paytm has a massive and diverse user base, including millions of consumers and merchants. Its wide adoption and user trust make it a preferred platform for digital payments and financial services in India.
- Brand Recognition: Paytm is a well-established and trusted brand in India. Its name is synonymous with digital payments, which further strengthens its position in the market.
- Diverse Service Offerings: Paytm offers a wide range of financial services, including digital payments, mobile wallets, e-commerce, insurance, mutual funds, and more. This diversification allows it to serve various consumer needs and preferences.
- User-Friendly Interface: Paytm’s user-friendly mobile app and website make it easy for users to perform transactions, pay bills, shop online, and access financial services. The intuitive interface enhances the user experience.
- Cashback and Rewards: Paytm has a robust cashback and rewards program. Users receive cashback incentives for various transactions, which encourages user engagement and loyalty.
- Digital Wallet: Paytm’s mobile wallet functionality allows users to store money digitally, reducing the need for physical cash. This is particularly beneficial in a country where digital payments are on the rise.
- Merchant Network: Paytm has an extensive network of merchants, both online and offline, that accept Paytm payments. This wide acceptance makes it convenient for users to use Paytm for various transactions.
- Investment and Expansion: Paytm has attracted substantial investments, including from Alibaba and Ant Financial, providing the financial resources needed for expansion, innovation, and technology development.
- Integration with Businesses: Paytm provides business solutions, including payment processing services and integration options for e-commerce and offline merchants. This integration simplifies payment acceptance for businesses.
- Financial Inclusion: Paytm contributes to financial inclusion in India by providing access to financial services to underserved populations. This aligns with the Indian government’s push for financial inclusion and digital payments.
- Regulatory Compliance: Paytm operates within the regulatory framework set by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and other relevant authorities. Compliance with regulations enhances trust among users and partners.
- Focus on Security: Paytm places a strong emphasis on security measures to protect user data and transactions. This commitment to security builds trust and confidence among users.
- Continuous Innovation: Paytm invests in innovation and technology to stay ahead in the rapidly evolving fintech landscape. This includes the development of new features, partnerships, and services.
- Digital Gold and Investment Products: Paytm’s offerings like digital gold and mutual fund investments provide users with accessible options for wealth creation and investment.
- Customer Support: Paytm offers customer support and assistance to address user queries and concerns promptly.
These competitive advantages have positioned Paytm as a leading player in the Indian digital payment and fintech industry. Its ability to offer a comprehensive suite of financial services, build user trust, and adapt to changing market dynamics has allowed it to maintain its market leadership and expand its user base over the years.
Critical Analysis of Business Model of PAYTM Company-
A critical analysis of Paytm’s business model reveals several strengths and weaknesses, as well as opportunities and threats in the competitive fintech and e-commerce landscape. Let’s examine these aspects in more detail:
Strengths:
- Diverse Service Offerings: Paytm’s diverse portfolio of services, including digital payments, mobile wallets, e-commerce, financial products, and utility bill payments, caters to a wide range of consumer needs. This diversification enhances user engagement and retention.
- Large User Base: Paytm boasts a massive and growing user base, which is a significant competitive advantage. Its strong presence in both urban and rural areas of India gives it a broad market reach.
- Brand Recognition and Trust: Paytm is a well-recognized and trusted brand in India. Users have confidence in the platform, which is crucial in the financial services sector.
- Cashback and Loyalty Programs: The company’s cashback and rewards programs incentivize users to transact through Paytm. This not only increases user engagement but also fosters loyalty.
- Digital Wallet: Paytm’s mobile wallet functionality addresses the need for digital alternatives to physical cash, aligning with the government’s push for a cashless economy.
- Merchant Network: Paytm has a vast network of merchants, making it a convenient payment option for consumers and encouraging merchant adoption.
- Investment and Innovation: Paytm’s access to significant investments and commitment to innovation enable it to stay competitive by introducing new features and services.
- Financial Inclusion: Paytm contributes to financial inclusion by offering access to financial services to those who are underserved or unbanked.
Weaknesses:
- Competition: The fintech and e-commerce sectors in India are highly competitive, with several players vying for market share. Staying ahead in this competitive landscape can be challenging.
- Regulatory Challenges: The fintech industry in India is subject to evolving regulations, which can impact business operations and necessitate compliance measures.
- Customer Acquisition Costs: Paytm has invested heavily in cashback incentives and marketing to acquire and retain users. High customer acquisition costs can affect profitability.
- Dependence on Investments: The company has relied on substantial investments from external sources, which may lead to pressures to achieve profitability and meet investor expectations.
Opportunities:
- Financial Services Growth: The growing popularity of digital financial services in India presents an opportunity for Paytm to expand its financial product offerings and attract more users.
- Rural and Semi-Urban Expansion: Penetrating deeper into rural and semi-urban areas offers significant growth potential, as these regions have substantial untapped markets.
- Government Initiatives: Government initiatives promoting digital payments, financial inclusion, and the cashless economy can provide a conducive environment for Paytm’s growth.
Threats:
- Competition: Competition from domestic and international players, including banks and fintech startups, poses a threat to Paytm’s market share.
- Regulatory Changes: Frequent changes in regulatory policies can impact fintech companies’ operations and compliance costs.
- Security and Data Privacy Concerns: With the increase in digital transactions, the risk of security breaches and data privacy issues is a significant threat.
- Profitability Challenges: Despite its growth, Paytm has faced profitability challenges. Achieving sustainable profitability in a competitive market can be a long-term challenge.
- Technology Disruption: Rapid advancements in technology could lead to disruptive innovations that challenge Paytm’s business model.
In conclusion, Paytm’s business model has several strengths, including its diverse service offerings, large user base, and brand trust. However, it also faces challenges related to competition, regulatory changes, and profitability. To sustain its growth and leadership in the Indian fintech and e-commerce space, Paytm must continue to innovate, expand its services, and address these challenges effectively.
Conclusion –
In conclusion, Paytm’s business model is a testament to the company’s remarkable journey from a mobile recharge and bill payment platform to a multifaceted fintech and e-commerce powerhouse. It has leveraged several strengths, including its diverse service offerings, large and diverse user base, and brand recognition, to establish itself as a leading player in the Indian digital payment and financial services industry.
However, Paytm also faces significant challenges, such as intense competition, regulatory changes, and profitability concerns. To continue its growth and maintain its competitive edge, Paytm must navigate these challenges effectively while capitalizing on opportunities like the growth of financial services and the expansion into underserved markets.
As the fintech and e-commerce sectors in India continue to evolve, Paytm’s ability to adapt, innovate, and provide value to its users will be critical to its long-term success. Its journey reflects the dynamism and potential of the digital economy in India, and it remains a company to watch as it continues to shape the future of digital payments and financial services in the country.